Since skin cancer is the most prevalent form of cancer in humans, much is written and said about it annually. Our skin is our largest organ, and certain parts of it are exposed to UV rays and other risk factors for skin cancer every day. In 2018, non-melanoma skin cancer was discovered in 3.604 Slovenians. Malignant melanoma is responsible for 90% of all skin cancer deaths and 15% of all skin cancers. Each year, about 600 people in Slovenia develop malignant melanoma. Melanoma, the most lethal type of skin cancer, will be the focus of this article.
WHAT CAUSES MELANOMA?
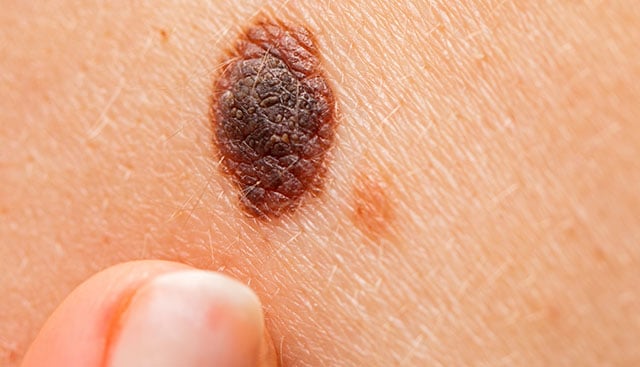
Melanoma originates in melanocytes, melanin-producing cells. The pigment in the skin is melanin. Healthy new cells push older cells toward the surface of the skin, where they die and eventually fall off, which is how skin cells normally develop in a controlled and orderly manner. But when DNA damage occurs in some cells, new cells can begin to grow uncontrollably, and eventually a mass of cancer cells can form. It is unclear what causes damage to the DNA in skin cells and how this leads to melanoma. Melanoma is most likely caused by a combination of environmental and genetic factors. However, melanoma is thought to be primarily caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from tanning beds and the sun. Factors of risk Skin that is fair or light has less melanin pigment, so it is less protected from UV rays. People with fair skin, blondes and redheads with light eyes and freckles are significantly more exposed than black people, which does not mean that black people cannot get melanoma.
a significant number of skin moles, including more than fifty atypical moles (dysplastic nevi) Sunburn of the skin with blisters (especially in childhood)
excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays (both in solariums and the sun) People who live near the equator and high in the mountains
Gender – it is more common in men
a family history of malignant melanoma. You are more likely to develop melanoma if a close relative (brother, sister, parents, etc.) has it. Weakened immune system. People with weakened immune systems have an increased risk of developing melanoma and other skin cancers. If you have a disease that weakens the immune system or take medications to suppress the immune system, such as after an organ transplant, your immune system may be weakened. Pigmentose Xeroderma Where can malignant melanomas be found? Melanoma occurs most frequently on skin that is exposed, such as the hands, face, ears, shins, and back. However, it rarely occurs on skin that is not exposed to sunlight. Reduce your exposure to the sun to lower your risk of developing melanoma. MELANOMA INSIDE AND OUT Melanoma in the eye. Ocular melanoma most often occurs in the uvea and can cause vision changes.
melanoma on the nail bed. A rare form of melanoma that occurs under the nails or toenails is called acaral-lentiginous melanoma. Additionally, on the soles and palms. Asians and black people have a higher prevalence. Melanoma in the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, and vagina, it is very difficult to detect them
UV light, therefore, does not cause all melanomas, especially those that appear on hidden parts of the body that have not been exposed to sunlight. This indicates that the development of melanoma may also be influenced by other factors.
SYMPTOMS AND SIGNALS A change in an existing mole
The appearance of a new mole or atypical growing change on your skin
Melanoma can appear as a newly formed change on healthy skin as well as from moles. Normal moles are round or oval, with clear edges, less than 6 mm in diameter and evenly colored. The majority of moles first appear in childhood. The majority of people have 10-40 moles. Only these can change in appearance over time, and with age, some may even vanish. The disease’s diagnosis and stage The diagnosis is based on the history of changing pigment marks, newly formed marks, exposure to the sun and burns, and dermatoscopic examination of the skin. We establish a definitive diagnosis with a biopsy and histopathological examination of the tissue.
The TNM system is used to determine the disease’s stage. According to Breslow and Clark, we determine the depth of invasion in a primary tumor. We will determine the presence of metastases in distant organs and the presence of macro- or micrometastases in regional lymph nodes through additional investigations. Based on the tests performed, we determine the stage of the disease and further treatment.
ESSENTIALS OF THERAPY Surgical excision of the entire lesion with a sufficient safety margin of healthy skin, depending on the thickness of the primary melanoma, is always the treatment for primary melanoma. We also treat metastatic lymph nodes surgically. Local irradiation of the tumor site or lymph nodes can supplement the surgical procedure if needed. There is no standard complementary treatment, but treatment with high-dose interferon is recommended. Targeted drugs that significantly improve survival quality and extend survival time have become available in recent years.
